Analysis of trusses by joint and section method
Numerical problem on the truss Analysis by the method of joints
Analyse the given truss given below by using the method of joints
Step 1: Converting the supports into reactions as shown in the figure below
Step 2: Check for Determinacy
w.k.t.
m+r-2j=0
9+3-2(6) =0
Therefore, the structure is determined.
Where,
m = The number of members in the structure
r = Support Reactions
j = Number of joints
Step 3: Calculation of support reactions
Number of unknown reactions = 3 (.i.e. HA, VA & VD)
Applying the equilibrium conditions
ΣH = 0
HA + 80 = 0 ……….. (1)
Therefore, HA = -80 KN
ΣV = 0
VA + VD = 50KN.............. (2)
Taking moment about support D
VA (3) – 50 (1) + 80 (0.75) = 0............. (3)
Solving the above equation
VA = - 3.33KN
Substitute VA in Eq (2)
Therefore, VD = 53.33 KN
Step 4: Free body diagram representing the nature of forces
Step 5: Solving joint A
Applying horizontal equilibrium condition
ΣH = 0
-80 + FAE + FAB Cosϴ = 0
(ϴ = Tan-1(0.75/1))
(ϴ = 36.86o)
FAE + FAB Cos36.86 = 80……… (1)
ΣV = 0
-3.33 + FAB Sinϴ = 0
FAB Sin36.86 = 3.33
Therefore, FAB = 5.55 KN (Tensile)…… (2)
Substitute (2) in (1)
FAE = 75.56KN(Tensile)
Step 6: Solving joint B
Applying horizontal equilibrium condition
ΣH = 0
FBC - FAB Sinα = 0
FBC – 5.55Sin 53.13 = 0
FBC = 4.44 KN
ΣV = 0
-FBE – FAB Cosα = 0
-FBE – 5.55Cos 53.13 = 0
FBE = -3.33KN
FBE = 3.33KN (Compression)
Step 7: Solving for joint E
ΣH = 0
- FAE + FEF + FEC Cosϴ = 0…… (1)
ΣV = 0
-FBE + FEC Sinϴ = 0
-3.33 + FEC Sin 36.86 = 0
FEC = 5.55KN (Tensile) ………. (2)
Substitute (2) in (1)
- FAE + FEF + FEC Cosϴ = 0
-75.56+ FEF +5.55Cos 36.86 = 0
Therefore, FEF = 71.12KN(Tensile)
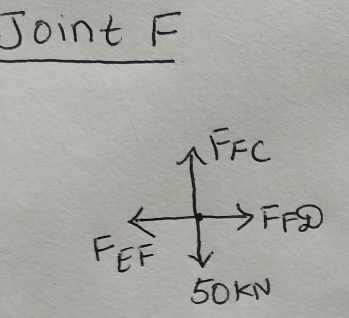
Step 8: Solving for joint F
ΣH = 0
FEF = FFD
FFD = 71.12KN (Tensile)
ΣV = 0
FFC = 50KN (Tensile)
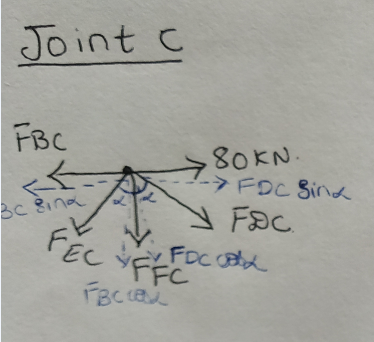
Step 9: Solving for joint C
ΣH = 0
-FBCSinα +80 + FDC Sinα = 0
-4.44Sin53.14 + 80 + FDC Sin53.14 = 0
FDC = - 95.55KN
FDC = 95.55KN (Compression)
Numerical problem on the truss Analysis by the method of Sections
Determine the forces in the member's BD, CD & CE
Step 1: Sectioning of a truss
Step 2: Check for Determinacy
w.k.t.
m+r-2j=0
. i.e., 7+3-2(5) =0
Therefore, the structure is determined.
Where,
m = The number of members in the structure
r = Support Reactions
j = Number of joints
Step 3: Determination of support reactions
Applying the equilibrium conditions
ΣH = 0
Therefore, HE = 0……… (1)
ΣV = 0
VA + VE = 8000 N…….. (2)
Taking moments about E
VA (2) + 4000 (1) – 1000 (1.5) – 3000(0.5) = 0
Therefore, VA = 3500N
Substitute (2) in (1)
VE = 4500N
Step 4: Determination of unknown forces
Taking moment about C
-VE (1) + 3000(0.5) – FDB (0.866) = 0
Solving the above equation,
FDB = -3464 N
FDB = 3464 N (Compressive)
Applying vertical equilibrium condition
ΣV = 0
-3000 - FDCSin60 + VE = 0
Therefore, FDC = 1732.05N (Tensile)
Taking Moments about D
-VE (0.5) +FCE (0.866) = 0
FCE = 2598N
Er. SP.ASWINPALANIAPPAN., M.E.,(Strut/.,)
Structural Engineer









No comments:
Post a Comment